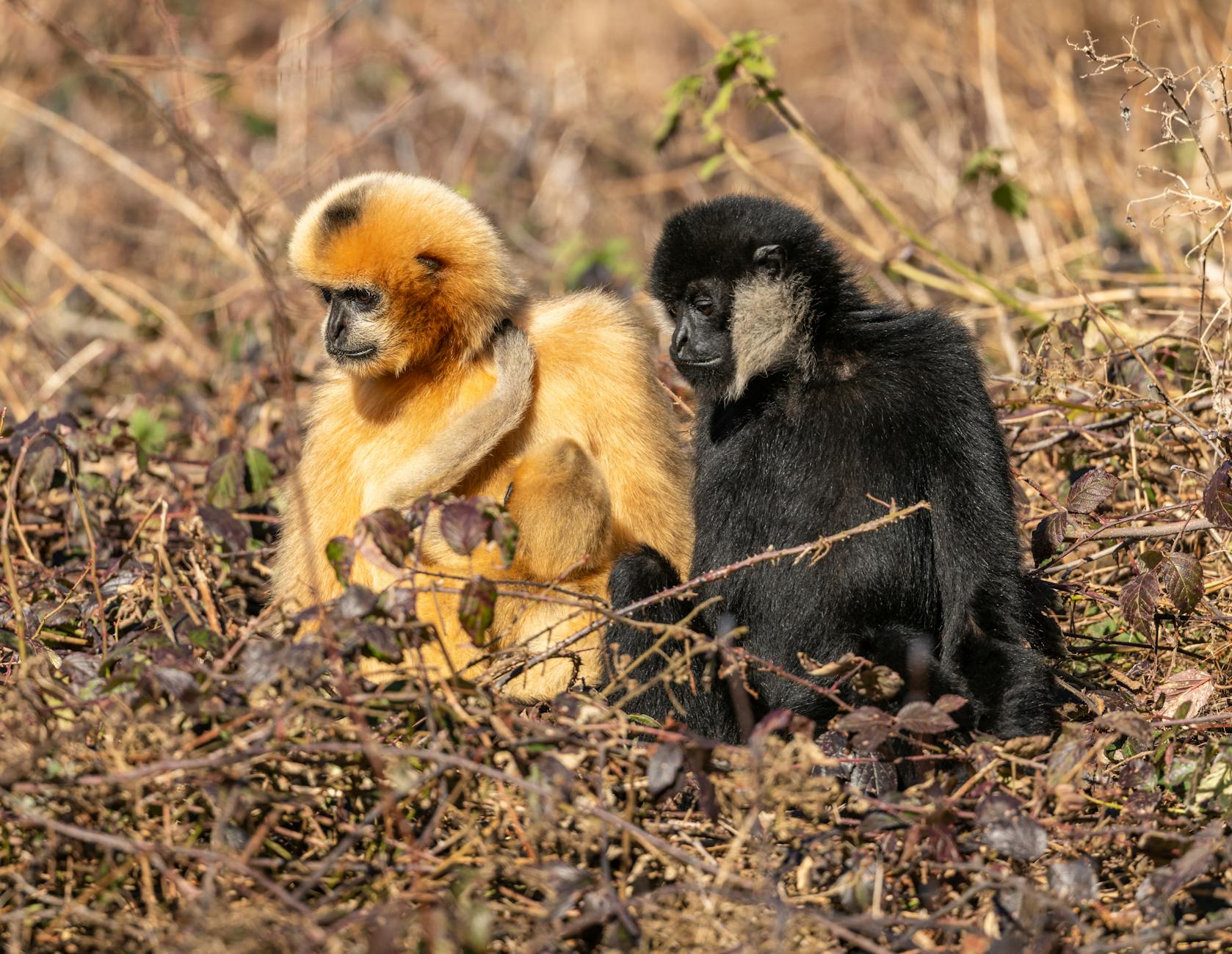
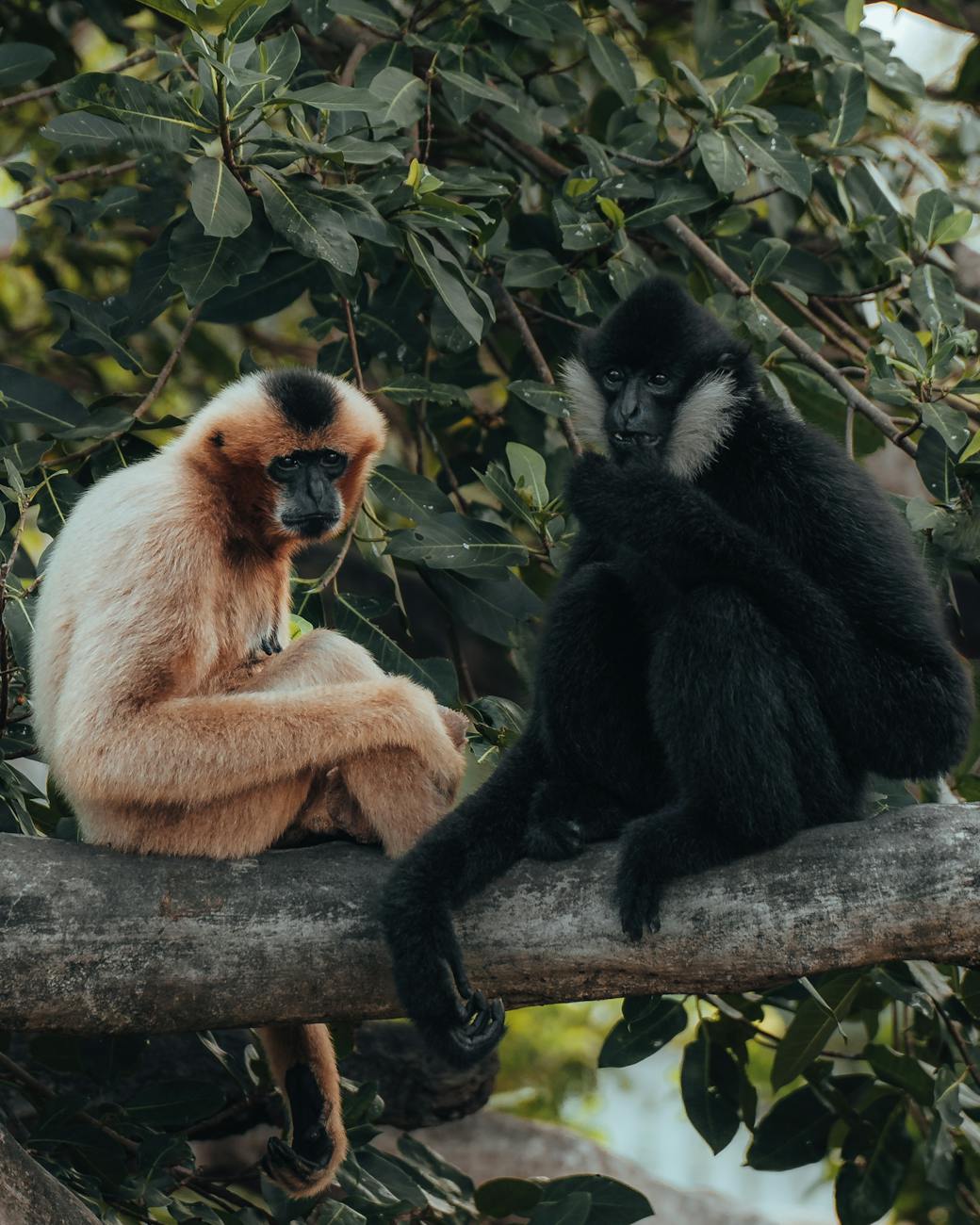
Hoolock gibbons are the only apes found in India, predominantly inhabiting the lush forests of NorthEast India. Belonging to the family Hylobatidae, these lesser apes are renowned for their distinctive songs and agile movement through the treetops.


Species and Distribution
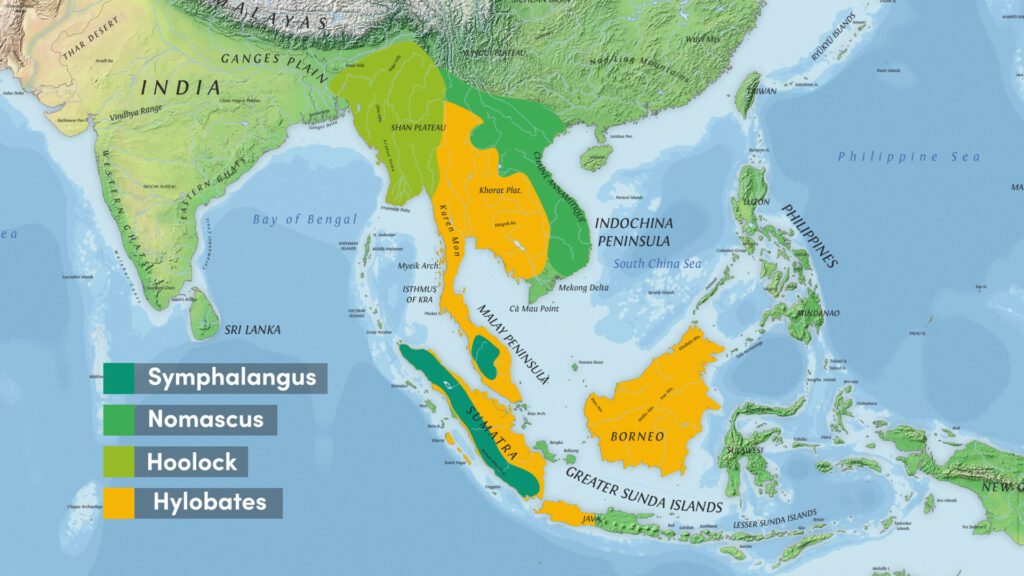
There are two species: Western Hoolock Gibbon (Hoolock hoolock) and Eastern Hoolock Gibbon ( Hoolock leucodedys)
Distribution
Habitat and Ecology
Habitat: Dense evergreen and semi-evergreen forests, often in hilly terrains.
Behavior:
• Arboreal and Diurnal: Spend most of their life in trees and are active during the day.
• Social Structure: Live in small family groups consisting of a monogamous pair and their offspring.
• Communication: Use loud calls or songs for communication and territory defense.
• Diet: Primarily frugivorous, consuming fruits, but also eat leaves, flowers, and insects.
Conservation Status
IUCN Red List: Both species are classified as Endangered due to rapid population declines.
Threats:
• Habitat Loss: Deforestation for agriculture, logging, and infrastructure development.
• Fragmentation: Loss of continuous forest leads to isolated populations.
• Hunting and Poaching: For meat and traditional medicine.
• Legal Protection: Listed under Schedule I of the Indian Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
Conservation Efforts
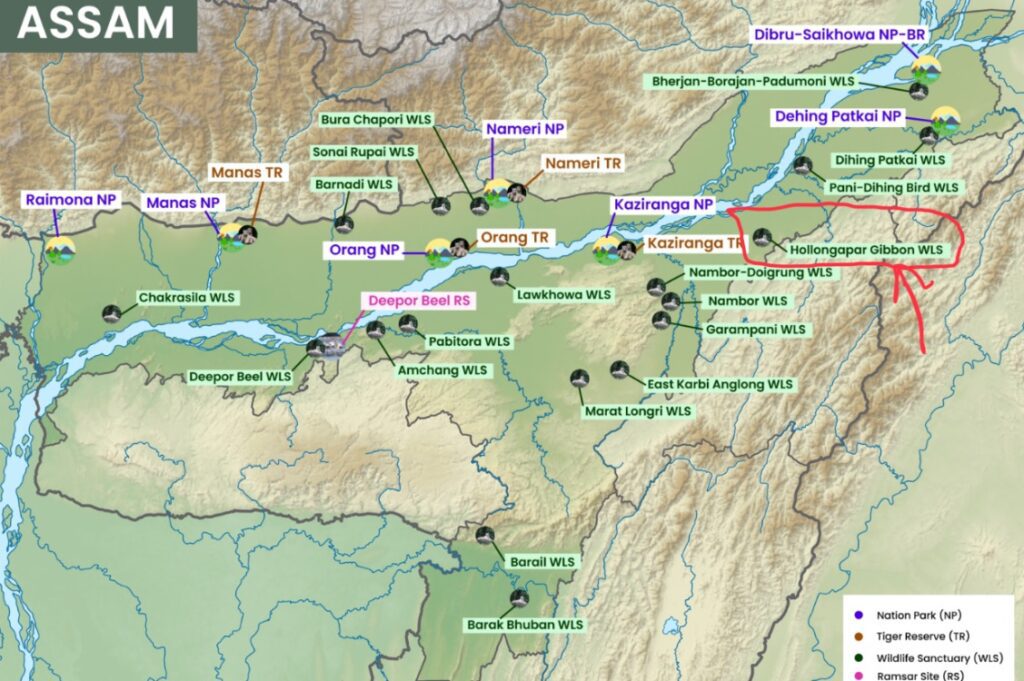
Protected Areas: Presence in sanctuaries like the Hoollongapar Gibbon Sanctuary in Assam.
• Community Involvement: Engagement of local communities in conservation initiatives.
• Reforestation Programs: Efforts to restore fragmented habitats.